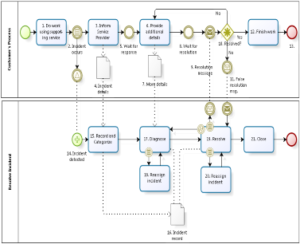
BPMN: a step toward automation I have argued elsewhere that the typical service management tools in use today might be suitable for service desk agents, but are annoying, redundant and of little value to anyone else involved in resolving incidents, among other activities. I have further proposed that existing IT management should be leveraged to […]
automation
Types of Tool Automation
Types of tool automation The fundamental difference between a software tool and most types of tools is that software can be programmed to automate one or more tasks. Most other tools do not automate work at all, only extending the capabilities of the wielder of the tool. Certain mechanical tools can automate a task, but, […]
What is a problem?
Although troubleshooting and the definitive elimination of faults has a long history, the particular innovation of ITIL® 2 was to recommend treating problems and incidents as two separate entities, each with its own life-cycle. This advice had led to a series of confusions and ambiguities, many of which have still not been resolved among the […]
The Automation of Risk Assessment
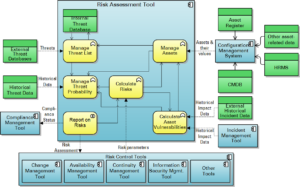
Pre-industrial risk assessment Risk assessment remains a highly manual activity in all organizations I have ever seen. Some organizations have a structured approach to assessing, and then managing, risk. Others work largely with a seat of the pants approach. But in both cases, the activity of identifying risks and their magnitude and the creation and […]
The scope of change control
With the publication of ITIL® ver. 3 in 2007, a clear stance was taken regarding the scope of change management. The authors of the Service Transition volume pointed out the rather obvious fact that changes at almost any place in the value network of service delivery could impact the quality of the services. Therefore, it […]